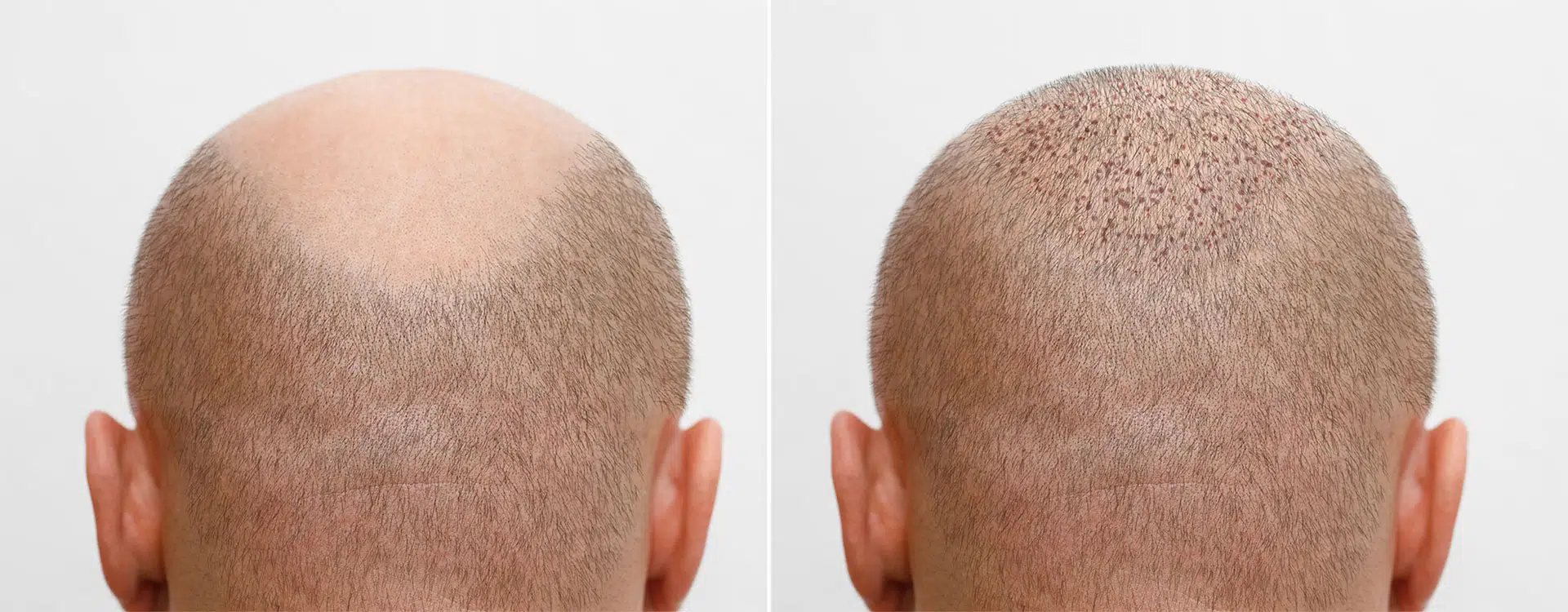
Hair loss is a common concern for many individuals, and advancements in medical science have provided various treatment options to address this issue. One of the most effective and widely sought-after treatments is hair transplantation. This procedure involves moving hair follicles from one area of the body, typically the back or sides of the scalp (known as the donor area), to the balding or thinning areas (known as the recipient area). But what is the science behind hair transplantation? In this article, we will explore the scientific principles that make hair transplantation a successful solution for hair loss.
Understanding Hair Growth: Before delving into the science behind hair transplantation, it’s important to understand the basics of hair growth. Hair follicles are small structures within the skin that produce hair. Each hair follicle undergoes a growth cycle consisting of three phases: anagen (active growth phase), catagen (transition phase), and telogen (resting phase). Hair loss occurs when the hair follicles enter a prolonged telogen phase or when the follicles miniaturise, resulting in thinning hair or bald patches.
Donor Dominance: The concept of donor dominance is fundamental to the success of hair transplantation. It refers to the observation that hair follicles taken from the donor area, which is typically resistant to the effects of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) – a hormone responsible for hair loss in androgenetic alopecia, will retain their genetic characteristics even when transplanted to the recipient area. This means that the transplanted hair will continue to grow naturally and resist the effects of DHT in the recipient area, providing long-term results.
Harvesting Techniques: There are two primary techniques used in hair transplantation: follicular unit transplantation (FUT) and follicular unit extraction (FUE). In FUT, a strip of scalp containing hair follicles is surgically removed from the donor area, and the individual hair follicles are then dissected under a microscope before being transplanted into the recipient area. FUE, on the other hand, involves the extraction of individual hair follicles directly from the donor area using a specialized tool. The choice of technique depends on various factors, including the patient’s specific needs and the surgeon’s expertise.
Graft Preparation: Once the hair follicles are harvested, they undergo meticulous graft preparation to ensure their viability and successful transplantation. The extracted follicles are carefully sorted and cleaned to remove excess tissue and debris. They are then preserved in a specialized solution to maintain their vitality and hydration until they are ready for transplantation. The quality of graft preparation plays a crucial role in the success of the procedure, as it ensures the survival and growth of the transplanted hair follicles.
Recipient Site Creation: Creating the recipient sites is a critical step in the hair transplantation process. The surgeon strategically makes tiny incisions or slits in the recipient area, considering factors such as the angle, depth, and density required to achieve a natural-looking result. The precise placement and orientation of the transplanted follicles are crucial to ensure proper hair growth and an aesthetically pleasing outcome. Advanced techniques, such as trichophytic closure, can also be employed to minimize scarring and enhance the natural appearance of the hairline.
Angiogenesis and Neovascularization: The success of hair transplantation depends on the establishment of a robust blood supply to the transplanted follicles. Angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels, and neovascularization, the process of creating a network of blood vessels, play a vital role in this regard. The recipient site’s blood supply gradually extends to the transplanted follicles, providing them with the necessary nutrients and oxygen for survival and growth. The science behind angiogenesis and neovascularization ensures the integration and sustainability of the transplanted hair follicles.
Post-Transplant Care: After the hair transplant procedure, proper post-transplant care is essential to support the healing process and promote the growth of transplanted hair. This typically involves following the surgeon’s instructions, including gentle washing and care of the recipient area, avoiding strenuous activities, and using prescribed medications or topical solutions. The science behind post-transplant care aims to create an optimal environment for the transplanted hair follicles to thrive and yield natural-looking results.
In conclusion, hair transplantation is a scientifically grounded procedure that offers an effective solution for hair loss. Understanding the principles of hair growth, donor dominance, harvesting techniques, graft preparation, recipient site creation, angiogenesis, neovascularization, and post-transplant care helps to appreciate the scientific foundation behind successful hair transplantation. By combining medical expertise, advanced techniques, and meticulous attention to detail, hair transplantation can restore natural hair growth and provide individuals with a renewed sense of confidence and well-being.